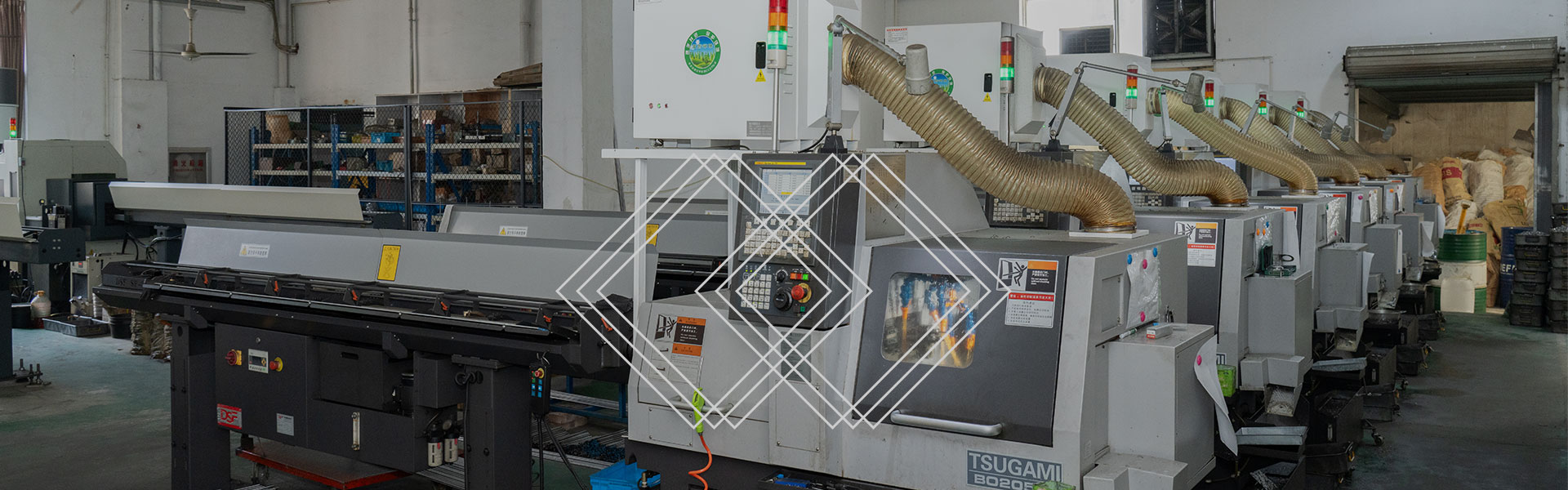
What is the difference between a solenoid and an electromagnet valve?
2024-11-27
Solenoid valves and solenoids have certain correlations in function and principle, but they are different in practical applications.

Solenoid valve
Definition: Solenoid valve is a medium switching component in the electromagnetic control industry. It uses electromagnetic force to control the movement of the valve core, thereby changing the passage inside the valve body to achieve the purpose of cutting off, connecting or changing the flow direction of the medium.
Structure: Solenoid valves are usually composed of electromagnetic coils, valve cores, valve bodies and other components.
Working principle: When the electromagnetic coil is energized, electromagnetic force is generated, which drives the valve core to move, thereby changing the passage state of the valve body. When the electromagnetic coil is de-energized, the valve core is usually restored to its initial position by a reset mechanism such as a spring.
Application scenario: Solenoid valves are widely used in industrial automation control systems, such as fluid control, air pressure control and other scenarios.
Solenoid
Definition: Solenoid is a device made using the principle of electromagnetic induction. When current passes through the wire, a magnetic field is generated around the wire. If the wire is wound into a solenoid shape, it is called an electromagnet or solenoid.
Structure: An electromagnet usually consists of a coil and an iron core. When the coil is energized, the iron core is magnetized to generate a magnetic field; when the coil is de-energized, the magnetism of the iron core disappears.
Working principle: The working principle of an electromagnet is based on the magnetic effect of current. When current passes through a wire, a magnetic field is generated around the wire, which can attract ferromagnetic materials (such as iron, cobalt, nickel, etc.).
Application scenarios: Electromagnets are widely used in a variety of electrical equipment such as relays, contactors, and solenoid valves.
In summary, although both solenoid valves and electromagnets use the principle of electromagnetic induction, they differ in structure, working principle, and application scenarios. Solenoid valves focus more on controlling the on/off and flow direction of the medium, while electromagnets focus more on generating magnetic fields and attracting ferromagnetic materials.