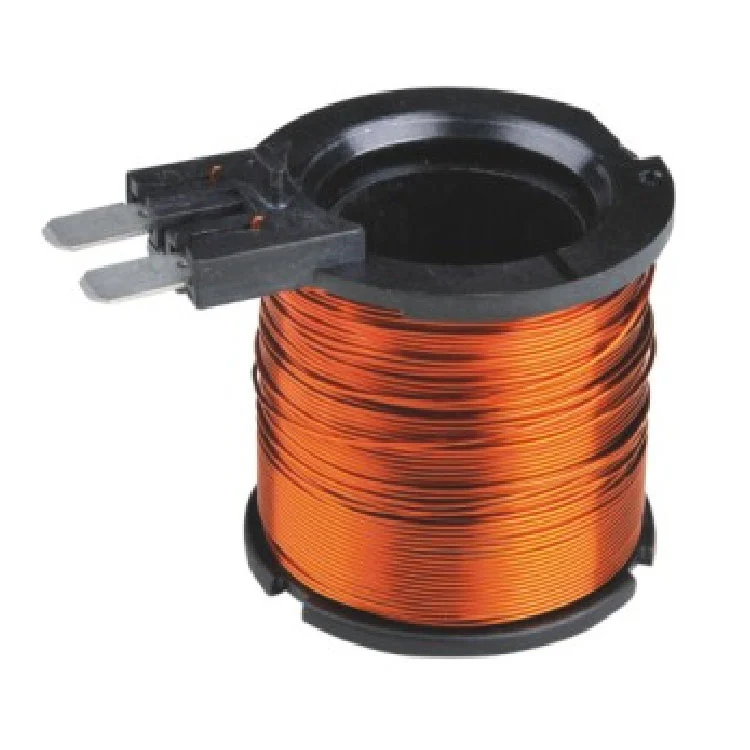
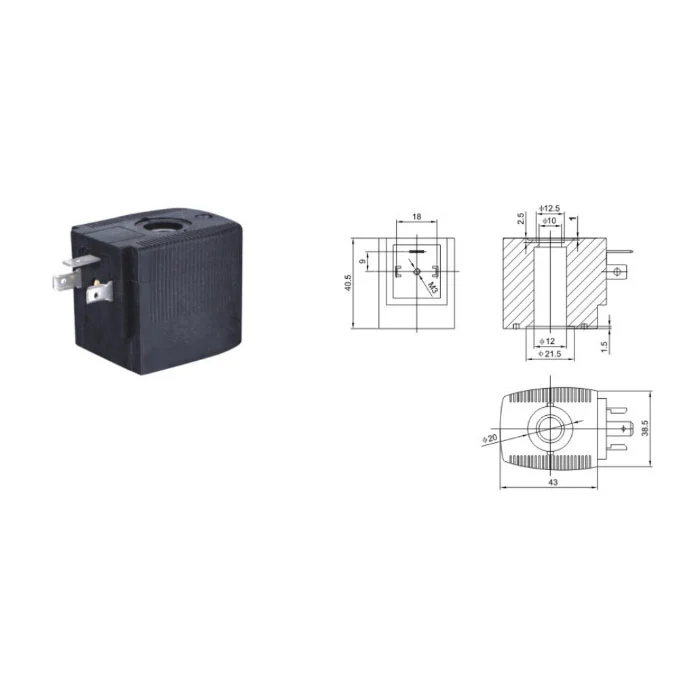
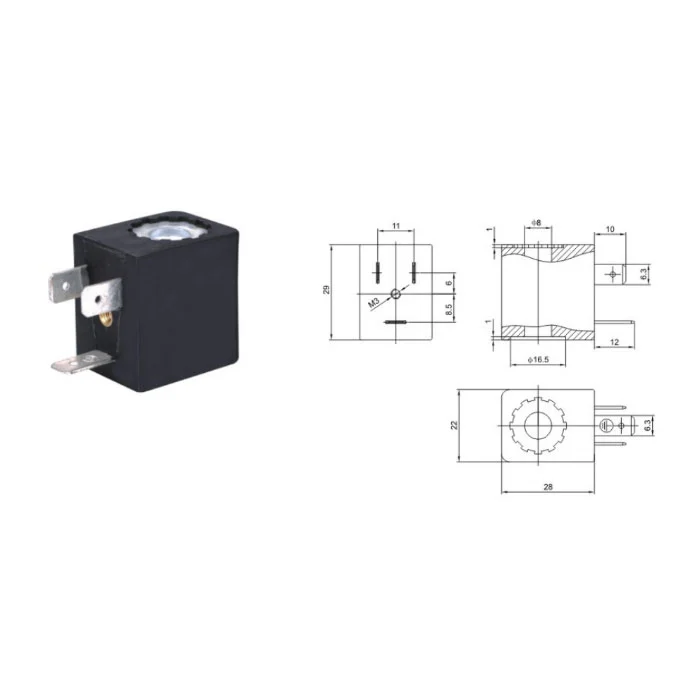
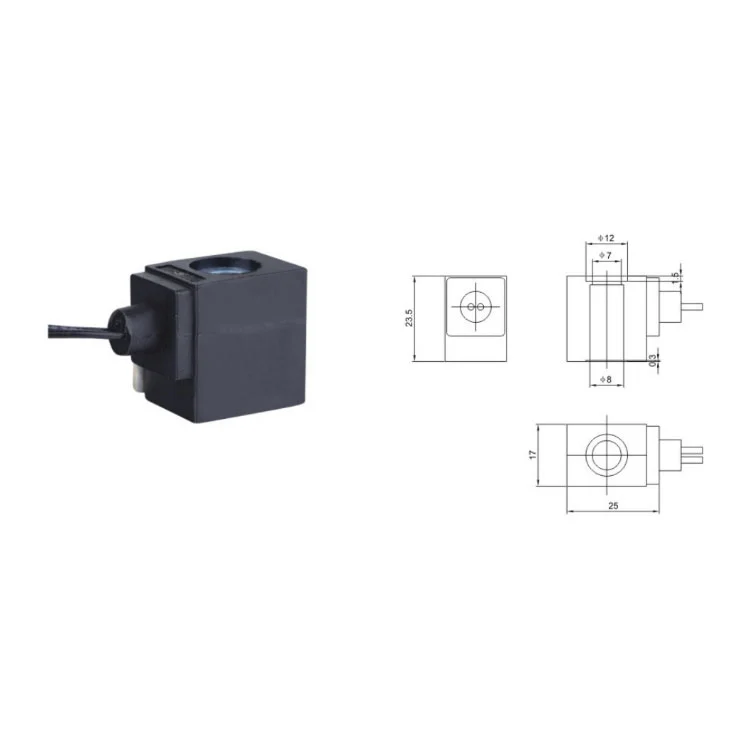
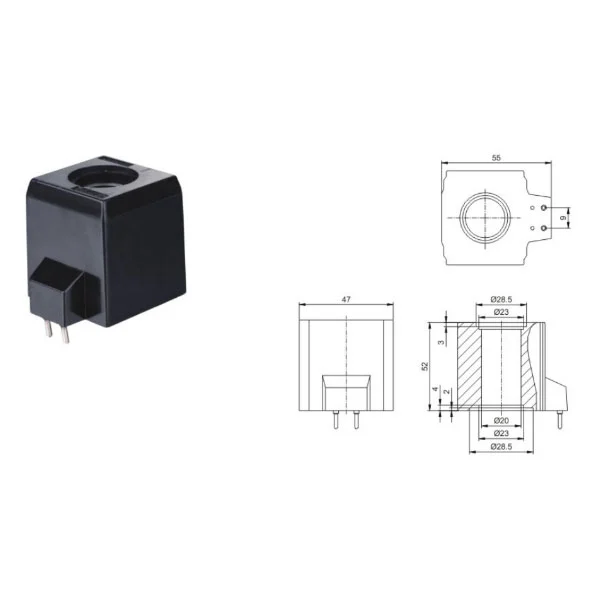
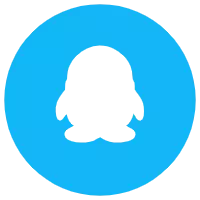
Solenoid Valve Coils
Send Inquiry
Solenoid Valve Coils have many types and characteristics. From the type of power supply, there are DC coils and AC coils. The DC coil usually has a stable magnetic field, which is suitable for the occasions where the control accuracy is required; Ac coils have certain advantages in terms of cost and versatility.
Specification:
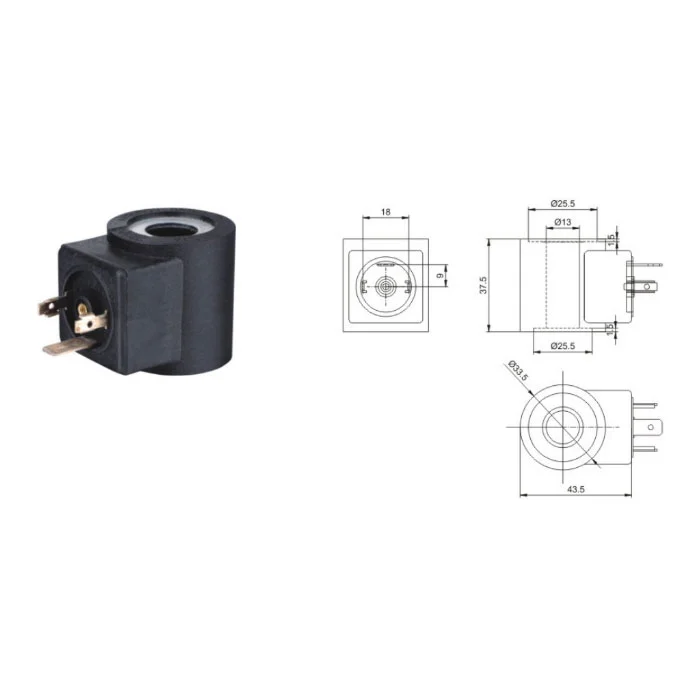
Item No: NC057 Overall Dimension

| Normal Voltage | AC220V AC110V DC24V DC12V | |
| Normal Power | AC | 16VA |
| DC | 15W | |
| Other voltage and power be customized | ||
| Insulation Class | B、 F、 H | |
| Connection type | DIN43650A | |
Details:
The working environment of the Solenoid Valve Coils also has an impact on its performance, such as temperature, humidity, pressure, etc. In harsh environments such as high temperature, humidity or high pressure, specially designed coils need to be selected to ensure proper operation.
Different models and specifications of solenoid valve coils are suitable for different application scenarios and working conditions, and need to consider factors such as system requirements, working environment and cost when selecting.
Product Feature:
1. Electromagnetic drive: The Solenoid Valve Coils magnetic field is generated by the current to achieve fast and accurate action control.
2. Rapid response: Solenoid Valve Coils can complete the movement of the spool in a short time to realize the rapid switching of the fluid channel.
3. Diverse power consumption: there are different power and current specifications to adapt to different power supplies and energy saving requirements.
4. Compact structure: small size, easy to install inside the solenoid valve, does not take up too much space.
5. Durability: The use of high-quality insulating materials and winding process, with good heat resistance, wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
Applications:
1. Industrial automation: used to control the flow of various liquids and gases, such as in the material transportation of production lines, cooling and lubrication systems of processing equipment.
2. Hvac system: adjust water flow and air flow to achieve temperature and humidity control.
3. Petrochemical industry: control the flow of pipeline intermediates, participate in the control and safety of the process.
4. Water treatment system: control the flow and direction of water to ensure the normal operation of the treatment process.
5. Automobile manufacturing: control of braking system, fuel injection system, etc.